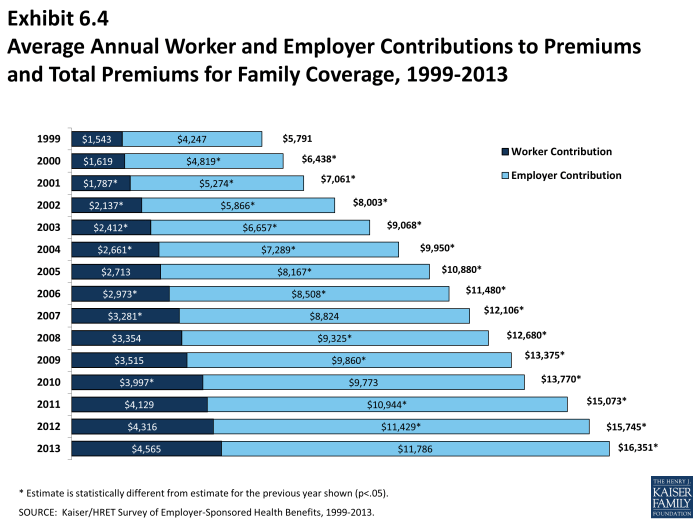
Cost of health insurance for self-employed sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Exploring the complexities of health insurance for self-employed individuals, this topic delves into the challenges and strategies associated with managing costs and coverage in today’s landscape.
As we navigate through the intricacies of health insurance options for self-employed individuals, it becomes evident that understanding the nuances of coverage and expenses is crucial for making informed decisions.
Introduction to Self-Employed Health Insurance Costs

Self-employment in the context of health insurance refers to individuals who work for themselves and do not have coverage through an employer-sponsored plan. These individuals are responsible for obtaining and paying for their own health insurance.
When it comes to international travel, having the right health insurance plan is crucial. With international health insurance plans , you can ensure that you are covered no matter where you go. Whether you’re on a short vacation or living abroad for an extended period, having the right coverage can give you peace of mind.
Health insurance is essential for self-employed individuals as it provides coverage for medical expenses, preventive care, and other healthcare needs. Without insurance, they may face financial challenges in accessing healthcare services and may be at risk of significant medical bills in case of illness or injury.
Understanding what is covered under Medicare Part A and B is essential for those eligible for these benefits. Medicare Part A and B cover different services, and knowing the details can help you make informed decisions about your healthcare needs. From hospital stays to preventive services, Medicare offers a range of coverage options.
Challenges Faced by Self-Employed Individuals
- Cost: Self-employed individuals often face higher health insurance costs compared to those covered by employer-sponsored plans. This can be a significant financial burden, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or older age.
- Limited Options: Due to their independent status, self-employed individuals may have limited options when it comes to choosing health insurance plans. They may not have access to group rates or benefits offered to employees of larger companies.
- Inconsistent Income: The fluctuating nature of self-employment income can make it challenging to budget for health insurance premiums. During slow periods, individuals may struggle to afford coverage, putting their health at risk.
- Complexity: Navigating the health insurance marketplace and understanding different plan options can be overwhelming for self-employed individuals who do not have a background in insurance. This complexity can lead to confusion and possible gaps in coverage.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Health Insurance for Self-Employed
When it comes to the cost of health insurance for self-employed individuals, there are several key factors that play a crucial role in determining the premiums they pay. These factors can vary from person to person and can significantly impact the overall cost of health insurance coverage. Let’s delve into some of the main influencers.
Age and Health Condition
Age and health condition are two major factors that can heavily influence the cost of health insurance for self-employed individuals. Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums compared to older individuals, as they are deemed to be at lower risk for health issues. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing health conditions may face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of needing medical care.
Chosen Coverage Options
The coverage options chosen by self-employed individuals can also have a significant impact on the overall cost of health insurance. Opting for a comprehensive plan with lower deductibles and copayments can result in higher premiums. On the other hand, choosing a high-deductible plan with lower premiums can lead to lower monthly costs but higher out-of-pocket expenses when medical care is needed.
Strategies to Manage Health Insurance Costs for Self-Employed
When it comes to managing health insurance costs as a self-employed individual, there are several strategies that can help you save money and maximize your benefits. One key aspect is understanding the benefits of health savings accounts (HSAs) and leveraging tax deductions related to health insurance premiums.
Benefits of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- HSAs allow you to set aside pre-tax money to pay for medical expenses, reducing your taxable income and lowering your overall tax bill.
- These accounts often come with high-deductible health plans, which typically have lower monthly premiums, making them a cost-effective option for self-employed individuals.
- Funds in an HSA can be rolled over from year to year, allowing you to build up savings for future healthcare expenses.
- Using an HSA to pay for qualified medical expenses means you won’t pay taxes on that money, providing additional savings.
Leveraging Tax Deductions for Health Insurance Premiums
- Self-employed individuals can deduct 100% of their health insurance premiums from their taxable income, reducing the amount of income subject to taxes.
- This deduction can lead to significant savings, especially for those who pay high premiums for comprehensive health coverage.
- Keep detailed records of your health insurance premiums and consult with a tax professional to ensure you are maximizing your deductions.
Comparison of Health Insurance Options for Self-Employed

When it comes to health insurance options for self-employed individuals, there are several choices available. It’s essential to understand the differences between individual plans, group plans, and marketplace options to make an informed decision that meets your needs and budget.
Individual Plans vs. Group Plans, Cost of health insurance for self-employed
Individual health insurance plans are purchased directly by individuals for themselves and their families. These plans offer customization options and flexibility in choosing coverage levels and benefits. On the other hand, group health insurance plans are typically offered by employers to their employees, including self-employed individuals with employees. Group plans often provide more comprehensive coverage at lower costs due to risk-sharing among a larger pool of individuals.
Marketplace Options like Healthcare.gov
Healthcare.gov is the federal health insurance marketplace where individuals, including self-employed individuals, can compare and purchase health insurance plans. Marketplace options provide access to a range of health insurance plans from different insurance companies, allowing individuals to compare costs and coverage options easily. Additionally, eligible individuals may qualify for subsidies to help lower the cost of premiums.
Understanding the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and Its Impact on Self-Employed Health Insurance Costs: Cost Of Health Insurance For Self-employed

The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, has significantly influenced the cost and availability of health insurance for self-employed individuals. By implementing various reforms and regulations, the ACA aimed to make health insurance more affordable and accessible for all Americans, including those who are self-employed.
Key Provisions of the ACA Affecting Self-Employed Individuals
- Marketplace Exchanges: The ACA established health insurance marketplaces where individuals, including the self-employed, can compare and purchase health insurance plans. These exchanges offer a range of options, providing more choices for self-employed individuals to find coverage that suits their needs and budget.
- Subsidies and Tax Credits: The ACA offers subsidies and tax credits to help lower-income self-employed individuals afford health insurance. These financial assistance programs can significantly reduce the cost of premiums, making coverage more accessible.
- Pre-Existing Conditions: The ACA prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. This provision ensures that self-employed individuals with pre-existing health issues can still obtain affordable insurance coverage.
- Essential Health Benefits: The ACA requires all health insurance plans to cover essential health benefits, including preventive care, prescription drugs, and maternity care. This ensures that self-employed individuals have access to comprehensive coverage that meets their healthcare needs.
Long-Term Implications of the ACA on Self-Employed Health Insurance Costs
The long-term implications of the ACA on self-employed health insurance costs are multifaceted. While the ACA has helped make insurance more affordable for many self-employed individuals through subsidies and marketplaces, there have been concerns about rising premiums and limited plan options in some regions. Additionally, changes in healthcare policies and regulations could impact the overall cost and availability of health insurance for self-employed individuals in the future.
In conclusion, the discussion on the cost of health insurance for self-employed sheds light on the importance of proactive planning and informed choices when it comes to securing adequate coverage. By implementing cost-saving strategies and exploring available options, self-employed individuals can navigate the complexities of health insurance with confidence and financial prudence.
Health insurance deductible vs. copay can be confusing for many people. While both are costs you pay out of pocket, they work differently. Understanding the differences between deductibles and copays can help you choose the right plan for your needs. Deductibles are the amount you pay before your insurance kicks in, while copays are fixed amounts you pay for services.