Kicking off with Health insurance plans for seniors, this guide provides a detailed look into the various options available, helping seniors navigate through the complexities of health insurance with ease.
Exploring the importance of coverage, different types of plans, and cost-saving tips, this article aims to equip seniors with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about their health insurance.
Overview of Health Insurance Plans for Seniors

Health insurance is crucial for seniors as it helps cover the high costs of medical care and provides financial protection in case of unexpected health issues. There are different types of health insurance plans available specifically designed to meet the healthcare needs of seniors, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance options.
Medicare
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger people with disabilities. It is divided into different parts, including Part A (hospital insurance), Part B (medical insurance), Part C (Medicare Advantage), and Part D (prescription drug coverage). Medicare provides coverage for a wide range of medical services and treatments, offering a level of financial security for seniors when it comes to healthcare expenses.
Medicaid
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that helps with medical costs for individuals with limited income and resources. While eligibility requirements vary by state, Medicaid provides coverage for a broad range of services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, long-term care, and more. Seniors who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid, known as “dual eligibles,” can benefit from the comprehensive coverage offered by both programs.
Private Insurance Options
Private health insurance plans for seniors are offered by commercial insurers and can be purchased directly or through the health insurance marketplace. These plans typically offer more flexibility and additional benefits compared to traditional Medicare plans. Seniors can choose from a variety of private insurance options, such as Medicare Supplement plans (Medigap), Medicare Advantage plans, and standalone prescription drug plans.
Overall, seniors have a range of health insurance options to choose from, each with its own benefits and coverage options. It’s important for seniors to carefully evaluate their healthcare needs and financial considerations to select the most suitable health insurance plan that meets their requirements.
Coverage Options

Medicare offers a variety of coverage options for seniors to help meet their healthcare needs. Let’s explore the coverage provided by Medicare Parts A, B, C, and D, as well as the benefits of supplemental insurance (Medigap) and the relevance of long-term care insurance for senior health coverage.
Medicare Parts A, B, C, and D
- Medicare Part A: Covers hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care services.
- Medicare Part B: Covers outpatient care, doctor visits, preventive services, and durable medical equipment.
- Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage): Offers an alternative way to receive Medicare benefits through private insurance companies, often including additional benefits like vision, dental, and prescription drug coverage.
- Medicare Part D: Provides prescription drug coverage to help seniors afford necessary medications.
Supplemental Insurance (Medigap)
- Medigap plans are sold by private insurance companies to help cover costs that Original Medicare (Parts A and B) doesn’t pay for, such as copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles.
- These plans can provide peace of mind by filling in the gaps left by Medicare, helping to reduce out-of-pocket expenses for seniors.
Long-Term Care Insurance
- Long-term care insurance helps cover expenses associated with services that assist with daily living activities, such as nursing home care, assisted living, and in-home care.
- It is important for seniors to consider long-term care insurance as it can help protect their savings and assets in case they require long-term care in the future.
Cost Considerations: Health Insurance Plans For Seniors

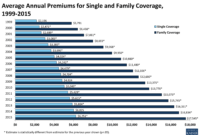
When it comes to health insurance plans for seniors, cost is a crucial factor to consider. Seniors need to analyze the costs associated with different plans to ensure they are getting the coverage they need at a price they can afford. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Comparing Premiums and Coverage
- Seniors should compare premiums and coverage options across different health insurance plans to find the best value for their needs.
- It’s important to consider not just the monthly premium, but also out-of-pocket costs like deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
- Some plans may have lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs, while others may have higher premiums but more comprehensive coverage.
Saving Money on Premiums
- Seniors can save money on health insurance premiums by choosing plans with higher deductibles or copayments, which typically have lower monthly premiums.
- Exploring Medicare Advantage plans, which often offer additional benefits like vision and dental coverage, can sometimes be more cost-effective than traditional Medicare.
- Taking advantage of discounts for healthy behaviors, such as not smoking or participating in wellness programs, can also help reduce premiums.
Financial Assistance Programs, Health insurance plans for seniors
- Seniors who need help covering health insurance costs can explore financial assistance programs like Medicaid, which provides coverage for low-income individuals.
- The Medicare Savings Programs offer assistance with premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance for seniors who meet certain income and asset requirements.
- Pharmaceutical assistance programs can help seniors afford prescription medications, which can be a significant cost for many older adults.
Enrollment Process
When it comes to enrolling in health insurance plans for seniors, understanding the enrollment process is crucial. Seniors have specific options available to them, such as Medicare and Medicaid, each with its own set of eligibility criteria and steps for enrollment.
Medicare Enrollment
Seniors who are 65 years old or older, or those who qualify due to certain disabilities, are eligible for Medicare. The enrollment process for Medicare typically begins three months before the individual turns 65 and extends for a total of seven months. This includes the initial enrollment period, special enrollment periods, and the general enrollment period. To enroll in Medicare, seniors can do so online through the Social Security website, by calling the Social Security office, or by visiting their local Social Security office in person.
Medicaid Enrollment
Medicaid is a state and federally funded program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals, including seniors. Eligibility for Medicaid varies by state, but seniors typically need to meet income and asset requirements to qualify. The enrollment process for Medicaid involves submitting an application through the state’s Medicaid agency. Seniors can apply online, by phone, by mail, or in person at the local Medicaid office.
Step-by-Step Guide for Enrollment
1. Determine eligibility: Understand the specific eligibility criteria for Medicare or Medicaid based on age, income, and other factors.
2. Gather necessary documents: Collect documents such as proof of age, citizenship, income, and assets for the enrollment process.
3. Choose a plan: Compare different health insurance plans available for seniors and select one that best fits your needs.
4. Enroll online or offline: Follow the specific instructions provided by Medicare or Medicaid to enroll in the chosen health insurance plan.
5. Review coverage: Once enrolled, review the coverage options and benefits provided by the chosen health insurance plan to ensure it meets your healthcare needs.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of health insurance plans for seniors is crucial for ensuring comprehensive coverage and financial security in later years. By exploring the options, costs, and enrollment process, seniors can make informed choices that prioritize their well-being and peace of mind.