Medicaid eligibility and cost take center stage in this comprehensive guide. Dive into the intricacies of Medicaid requirements and financial implications to gain a deeper understanding of this crucial topic.
Explore the nuances of Medicaid eligibility criteria, application processes, cost-sharing mechanisms, and the impact of Medicaid expansion in this detailed discussion.
Medicaid Eligibility Criteria: Medicaid Eligibility And Cost
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to individuals with low income and limited resources. To qualify for Medicaid, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including income limits and asset restrictions.
Income Limits and Asset Restrictions
In general, Medicaid eligibility is based on income, family size, and the specific Medicaid program in each state. Income limits vary depending on the program and may change annually. Asset restrictions also apply, meaning individuals must have limited assets to qualify for Medicaid.
Comparison of Eligibility Criteria Across States
Each state has its own Medicaid program with varying eligibility criteria. Some states have expanded Medicaid eligibility under the Affordable Care Act, while others have more restrictive criteria. It’s important to check the specific requirements in your state to determine if you qualify for Medicaid coverage.
Application Process

When applying for Medicaid, there are specific steps to follow to ensure a smooth process. It is important to have all the necessary documentation ready to provide accurate information for eligibility determination.
Documentation Required, Medicaid eligibility and cost
- Proof of identity (such as a driver’s license or passport)
- Social Security number
- Proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns, etc.)
- Proof of residency (utility bills, lease agreement, etc.)
- Information on any other health insurance coverage
Tips for Application
- Start by gathering all the required documentation before beginning the application process.
- Fill out the application form completely and accurately to avoid delays in processing.
- If you need assistance, reach out to a Medicaid office or healthcare provider for guidance.
- Follow up on your application status to ensure it is being processed in a timely manner.
- Keep copies of all documents submitted for your records.
Medicaid Cost Sharing

Medicaid cost sharing refers to the expenses that Medicaid beneficiaries may be required to pay for certain medical services or prescriptions. These costs are meant to help offset some of the program’s expenses and encourage responsible use of healthcare services.
Types of Costs Covered by Medicaid
- Co-payments: These are fixed amounts that beneficiaries must pay for specific services or medications.
- Premiums: Some Medicaid beneficiaries may be required to pay a monthly premium to maintain their coverage.
- Deductibles: Certain Medicaid plans may have deductibles, which are the amounts beneficiaries must pay out of pocket before Medicaid coverage kicks in.
Medicaid Expansion

Medicaid expansion refers to the provision in the Affordable Care Act that allows states to broaden their Medicaid programs to cover more low-income individuals. This expansion has had a significant impact on both eligibility and cost within the program.
States that have Expanded Medicaid
- As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia have expanded Medicaid, providing coverage to millions of low-income adults who were previously ineligible.
- States like California, New York, and Michigan have seen a significant increase in Medicaid enrollment and a decrease in the uninsured rate due to expansion.
Outcomes of Medicaid Expansion
- Research has shown that Medicaid expansion has led to improved access to healthcare services, better health outcomes, and reduced financial strain on individuals and families.
- States that have expanded Medicaid have also experienced cost savings as more individuals have access to preventive care, reducing the need for expensive emergency services.
Benefits and Challenges of Medicaid Expansion
- Benefits: Medicaid expansion has helped close the coverage gap for low-income individuals, improved health equity, and stimulated the economy by creating jobs in the healthcare sector.
- Challenges: Some states have faced opposition to expansion due to concerns about costs and sustainability, as well as political disagreements over the role of government in healthcare.
In conclusion, navigating the realm of Medicaid eligibility and cost can be complex, but with the right knowledge and guidance, individuals can access the healthcare benefits they need. Stay informed and empowered to make informed decisions regarding your Medicaid coverage.
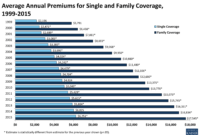
Understanding health insurance premiums can be complex, but it is essential for individuals to grasp the factors that influence their costs. Factors such as age, location, and coverage level can all impact the amount you pay for health insurance. By understanding how these premiums are calculated, individuals can make informed decisions when selecting a plan that best suits their needs and budget.
HMOs typically cover a wide range of services, including preventive care, hospital stays, and prescription drugs. However, it is essential to understand the limitations of an HMO, such as the need for referrals to see specialists and restrictions on out-of-network care. By knowing what an HMO covers, individuals can make the most of their health insurance benefits while avoiding unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
When it comes to outpatient services under health plans , coverage can vary significantly depending on the type of plan you have. Some plans may cover a wide range of outpatient services, including doctor visits, lab tests, and physical therapy, while others may have more limited coverage. Understanding your plan’s coverage for outpatient services is crucial for managing your healthcare costs and accessing the care you need.